We are presenting Class 6 SST Question Bank for Term-2.This Question bank is very useful for students of class 6 for annual exam preparation. Question bank is prepared as per new pattern and marking scheme of KVS.This Question bank are very useful for teachers of KVS,CBSE schools and schools following NCERT syllabus.
Class 6 SST Question Bank (Term-II)

Dear teachers and educators we are presenting Class 6 SST Question Bank for Term-2. Thus question bank is prepared according to new syllabus and pattern of KVS. In this question bank all important questions from Geography – Our Environment Part-1, History -Our Pasts Part -1 and Political Science – Social and Political Life Part-1 will be covered as per blueprint of Annual Exam.
Class 6 SST Question Bank – BLUE PRINT
| KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, BLUE PRINT FOR SOCIAL SCIENCE | |||||
| CLASS VI SESSION ENDING EXAM (2022-23) | |||||
| TIME : 2 Hours 30 min | Maximum marks =60 | ||||
| NAME OF THE LESSON CCT | VSA(1) | SA(3) | LA(5) | MAP | TOTAL |
| HISTORY | – | – | – | – | – |
| 1. WHAT, WHERE, HOW AND WHEN | – | – | – | – | – |
| 2. ON THE TRAIL OF THE EARLIEST | – | – | – | – | – |
| 3. FROM GATHERING TO GROWING FOOD | – | – | – | ||
| 4. IN THE EARLIEST CITIES | – | – | – | – | – |
| 5. WHAT BOOKS AND BURIALS TELL US? 1×4 | – | – | – | – | 4 |
| 6. KINGDOMS, KINGS AND AN EARLY REPUBLIC | – | – | – | – | – |
| 7. NEW QUESTIONS AND IDEAS | – | – | – | – | – |
| 8. ASHOKA THE EMPEROR WHO GAVE UP WAR | 1X1 | – | 1X2 | 3 | |
| 9. VITAL VILLAGES THRIVING TOWNS | 1X1 | – | – | – | 1 |
| 10. TRADERS, KINGS AND PILIGRIMS | 1X5 | – | 5 | ||
| 11. NEW EMPIRES AND KINGDOMS | 1X2 | 1X3 | – | – | 5 |
| 12. BUILDINGS, PAINTINGS AND BOOKS | 1X2 | – | 2 | ||
| 4 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 20 |
| GEOGRAPHY | – | – | – | – | – |
| 1. THE EARTH IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM | – | – | – | – | – |
| 2. GLOBE: LATITUDES AND LONGITUDES | – | – | – | 1X2 | 2 |
| 3. MOTIONS OF THE EARTH | – | – | – | – | – |
| 4. MAPS | – | – | – | ||
| 5. MAJOR DOMAINS OF THE EARTH 1×4 | 1X1 | – | – | 5 | |
| 6. MAJOR LANDFORMS OF THE EARTH | 1X2 | 2 | |||
| 7. OUR COUNTRY- INDIA | 1X2 | 1X3 | 5 | ||
| 8. INDIA: CLIMATE, VEGETATION AND WILDLIFE | 1X1 | 1X5 | 6 | ||
| 4 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 20 |
| CIVICS | – | – | – | – | – |
| 1. UNDERSTANDING DIVERSITY | – | – | – | – | – |
| 2. DIVERSITY AND DISRIMINATION | – | – | – | – | – |
| 3. WHAT IS GOVERNMENT? | 1X1- | – | – | – | 1 |
| 4. KEY ELEMENTS OF A DEMOCRATIC GOVERNMENT | – | – | – | – | – |
| 5. PANCHAYATI RAJ 1×4 | – | – | – | 4 | |
| 6. RURAL ADMINISTRATION | – | – | |||
| 7. URBAN ADMINISTRATION | 1X1 | 1X3 | – | 4 | |
| 8. RURAL LIVELIHOOD | 1X1 | 1X5 | – | 6 | |
| 9. URBAN LIVELIHOOD | – | – | 1X5 | – | 5 |
| 4 | 3 | 3 | 10 | – | 20 |
| 12 | 15X1=15 | 3X3=9 | 4X5=20 | 2X2 =4 | 60 |
Class 6 SST Question Bank– ASHOKA THE EMPEROR WHO GAVE UP WAR (3 Marks)
Very shorts answer type question- 01
Map Work-02 Marks
Very shorts answer type questions-
1. Complete the following sentences:
- Officials collected…….. from the area under the direct control of the ruler.
- Royal princes often went to the provinces as………….
- The Mauryan rulers tried to control…….. and……….. which were important for transport.
- People in forested regions provided the Mauryan officials with…………
Ans:
- taxes
- governors
- roads, rivers
- elephants, timber, honey, and wax.
2. State whether true or false:
- Ujjain was the gateway to the north-west.
- Chandragupta’s ideas were written down in the Arthashastra.
- Kalinga was the ancient name of Bengal
- Most Ashokan inscriptions are in the Brahmi script.
Ans:
- False
- True
- False
- True.
3. I. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct option to complete the statements given below:
(i) The founder of the Maurya empire was ………….,
(a) Ashoka
(b) Chandragupta
(c) Bimbisara
(d) Chanakya.
(ii)The capital of the Mauryan empire was………….
(a) Pataliputra
(b) Rajagriha
(c) Ujjain
(d) Taxila.
(iii) According to the Arthashastra, blankets of………… India was famous.
(a) north
(b) north-west
(c) south
(d) north-east.
(iv) The script used for inscription was ……………
(a) Brahmi
(b) Prakrit
(c) Tamil
(d) Roman.
(v) Ashoka was a ………………
(a) Hindu
(b) Jaina
(c) Buddhist
(d) None of these.
Ans.
(i)—(b), (ii)—(a), (iii)—(b), (iv)—(a), (v)—(c).
II. FILL IN THE BLANKS
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence.
- Ashoka was Chandragupta’s ……………………………….
- Chanakya was …….. ’s minister.
- The Arthashastra was written by………….
- …….. was the gateway to the northwest of the empire.
- ……… were sent as governors to other provincial capitals.
- South India was important for ………….
- Ashoka gave up war after winning over…………
- ‘Dhamma’ is the Prakrit word for the Sanskrit word
- Ashoka appointed …….. to spread ‘dhamma’.
Answer:
- grandson
- Chandragupta
- Chanakya
- Taxila
- Royal princes
- gold and other precious stones
- Kalinga
- ‘Dharma’
- officials.
III. TRUE/FALSE
State whether these sentences are true (T) or false (F).
- The lions on the currency notes come from the Rampurwa bull capital,
- Ashoka founded the Mauryan empire.
- Royal princes were sent as governors to provinces.
- Ashoka gave up war after losing in Kalinga.
- Ashoka himself went from place to place to preach ‘dhamma’.
- The ‘dhamma’ also reached other countries.
Ans.
- F
- F
- T
- F
- F
- T
IV. MATCHING SKILL
Match the items in column A correctly with those given in column B.

Map Work-02 Marks
All map related questions will be asked from the following map–
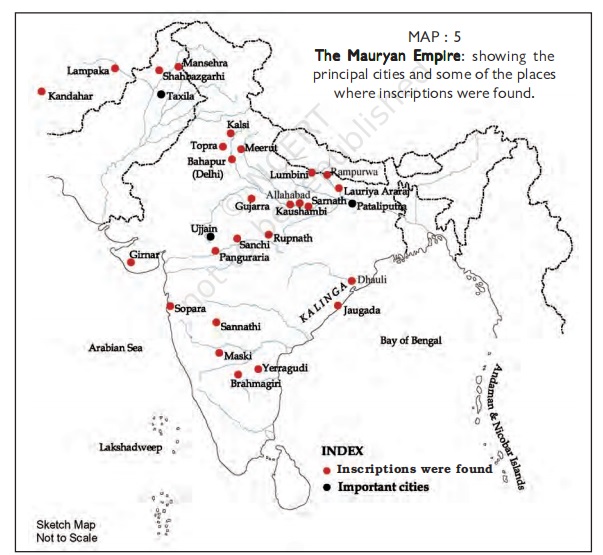
Class 6 SST Question Bank-VITAL VILLAGES THRIVING TOWNS (1 Mark )
Very shorts answer type question- 01
Question-1
Fill in the blanks:
- ……. was a word used for large landowners in TamiL
- The ‘gramabhojaka’ often got his land cultivated by the…………………..
- Ploughmen were known as ………….. in Tamil .
- Most ‘grihapatis’ were………….
Answer:
- ‘Vellalar’
- slaves and workers
- ‘uzhavar’
- smaller.
Question-2
Choose the correct answer:
(a) Ring wells were used for:
1. bathing
2. washing clothes
3. irrigation
4. drainage.
(b) Punch marked coins were made of:
1. Silver
2. gold
3. tin
4. ivory.
(c) Mathura was important:
1. village
2. port
3. religious centre
4. forested area.
(d) ‘Shrines’ were associations of:
1. rulers
2. crafts persons
3. farmers
4. herders.
Answer:
(a) drainage
(b) silver
(c) religious centre
(d) crafts persons.
. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Class 6 SST Question Bank
Choose the correct option to complete the statements given below:
(i) The use of iron in the Indian Subcontinent began about.
(a) 2000 years ago
(b) a million years ago
(c) 3000 years ago
(d) 500 years ago.
(ii) VeUalar was the term used for
(a) Large landowners
(b) Small farmers
(c) Common people
(d) Slaves.
(iii) Grambhojaka was a powerful man. He also worked as a
(a) Judge
(b) Policemen
(c) Councillor
(d) Both (a) and (b)
(iv) Mathura is an important centre for worship of
(a) Lord Rama
(b) Lord Krishna
(c) Lord Vishnu
(d) Both (a) and (b).
(v) Between 2200 and 1900 years ago, Arikamedu was a
(a) Coastal settlement
(b) Monastery
(c) Religious place
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(i)—(c), (ii)—(a), (iii)—(d), (iv)—(b), (v)—(a).
II. FILL IN THE BLANKS Class 6 SST Question Bank
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence.
- The post of grambhojaka was …………….
- There were independent farmers also who were known as ……………………
- …… literature was popular in Tamil Nadu.
- The Jatakas were stories preserved by …………………
- The associations of craftspersons and merchants were known as ……………………….
- Stamped red-glazed pottery was known as ………………. ware.
Answer:
- hereditary
- grihpatis
- Sangam
- Buddhist monks
- shrines
- Arretine.
III. TRUE/FALSE Class 6 SST Question Bank
State whether these sentences are true (T) or false (F).
- The plough share was used to increase agricultural production.
- Most of the grihpatis were large landowners.
- Extremely fine pottery was found in the southern part of the sub-continent,
- Shrines also served as banks where rich men and women deposited money,
- Arretine Ware was named after a city in Germany.
Answer:
- True
- False
- False
- True
False.
IV. MATCHING SKILL

Class 6 SST Question Bank TRADERS, KINGS AND PILGRIMS (5Marks)
Long answer type question 5 Marks
Question 1.Why did kings want to control the Silk Route?
Answer:Kings wanted to control the Silk Route because they could benefit from taxes, tributes and gifts that were brought by traders and the pdople along the route.
Question 2.What kinds of evidence do historians use to find out about trade and trade routes? Class 6 SST Question Bank
Answer:The historians use the following evidences to find out about trade and trade routes:
1. Archaeologists have collected information about the Northern Black Polished Ware. They have provided information about bowls and plates which were found from several sites throughout the subcontinent. They guess that traders might have been carried from the place where they were made, to other places.
2. Historians find evidence of trade in Sangam poems (or literary works). Here is one example which describes the goods brought into Puhar an important port on the east coast:
- Swift prancing horses by sea in ships
- bales of black pepper in carts
- gems and gold born in the Himalayas
- sandalwood born in the western hills
- the pearls of the southern seas
- corals from the eastern occeans
- the yield of the Ganga and the crops from the Kaveri
- foodstuffs from Sri Lanka
- pottery from Myanmar and other rare and rich imports.
Question 3.What were the main features of Bhakti? Class 6 SST Question Bank
Answer:
- Bhakti is generally understood as a person’s devotion to his or her chosen deity.
- The idea of Bhakti is present in the Bhagavad Gita, a sacred book of the Hindus.
- In the Bhagavad Gita (which is included in the Mahabharata), Krishna the God, asks Arjuna, his devotee and friend, to abandon all dharmas and take refuge in him, as only he can set Arjuna free from every evil.
- Those who followed the system of Bhakti emphasized devotion and individual worship of a single god or goddess, rather than the performance of elaborate sacrifices.
- Deities who were worshipped through Bhakti included Shiva, Vishnu and goddesses such as Durga. This form of worship became an important feature of Hinduism.
Question 4.Discuss the reasons why the Chinese pilgrims came to India?
Answer:The Chinese pilgrims (Fa-Xian, Xuan Zang and I-Qing) came to India to visit places associated with the life and teachings of the Buddha as well as famous monasteries. They had in Buddhist religious books also. They carried some books back with them.
Question 5.Why do you think ordinary people were attracted to Bhakti? Class 6 SST Question Bank
Answer:
- I think that ordinary people were attracted to Bhakti because Bhakt-saint used the language of people, which they could understand easily.
- The saints emphasized the worship of certain deities, which became a central feature of later Hinduism, gained in importance.
- These deities included Shiva, Vishnu and goddesses such as Durga. Bhakti is generally understood as a person’s devotion to his or her chosen deity.
- Anybody, whether rich or poor, belonging to the so called ‘high’ or ‘low’ castes, man or woman, could follow the path of Bhakti.
- They stressed on simple ways for Moksha or salvation, the last aim of life.
Class 6 SST Question Bank -NEW EMPIRES AND KINGDOMS (3 Marks)
2 very short answer type questions each of 1 mark and 1 short answer type question of 2 marks will be asked from this chapter in final exam. Class 6 SST Question Bank
Question 1. Class 6 SST Question Bank
State whether true or false:
- Harishena composed a prashasti, in praise of Gautamiputra Shri Satakarni.
- The rulers of Aryavarta brought tribute for Samudragupta.
- There were twelve rulers in Dakshinapatha.
- Taxila and Madurai were important centres under the control of the Gupta rulers.
- Aihole was the capital of the Pallavas.
- Local assemblies functioned for several centuries in south India.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True.
I. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Class 6 SST Question Bank
Choose the correct option to complete the statements given below:
(i) The first ruler of the Gupta dynasty who adopted the grand title of maharaj- adhiraja was
(a) Samudragupta
(b) Chandragupta
(c) Skandhagupta
(d) Both (a) and (c).
(ii) We learn about Gupta rulers from the
(a) Inscriptions
(b) Prashastis
(c) Coins
(d) Both (a) and (c).
(iii) Harsha’s brother-in-law was the ruler of
(a) Kanauj
(b) Patliputra
(c) Ujjain
(d) Prayaga.
(iv) Pulakeshin II was a ruler of
(a) Chalukya dynasty
(b) Pallava dynasty
(c) Gupta dynasty
(d) Chola dynasty,
(v) We come to know about Harshavardhana from
(a) The biography was written by Banabhatta
(b) The account of Xuan Zang
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (d).
Ans.
(i) – (b), (ii) – (d), (iii) – (a), (iv) – (a), (v) – (c).
II.FILL IN THE BLANKS Class 6 SST Question Bank
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence.
- Kumara Devi, the mother of Samudragupta belonged to the …………………… gana.
- ……………., a Chinese pilgrim, spent a lot of time at Harsha’s court and left a detailed account of what he saw.
- Harshavardhana’s success was checked by ………………., a chalukya ruler.
- The two important ruling dynasties in south India during this period were the ………. and the ………..
- The Raichur Doab was situated between the rivers …………………. and ………….
- The ……… and ……….. were the new dynasties which took place of the Pallavas and the Chalukyas.
- Whenever the Samantas found the ruler weak and inefficient, they tried to become
- The untouchables during this period were treated badly and were expected to live on the of the city.
Answer:
- Lichchhavi
- Xuan Zang
- Pulakeshin II
- Pallavas, Chalukyas
- Krishna, Tungabhadra
- Rashtrakuta, Chola
- independent
- outskirts
III.TRUE/FALSE Class 6 SST Question Bank
State whether these sentences are true (C) or false (F).
- The military leaders collected revenue from the land granted to them and spent this on their families.
- The rulers of dakshinapatha surrendered to Samudragupta after being defeated and were never allowed to rule again.
- The descendants of the Kushanas and Shakas ruled the outlying areas during this period.
- Harshavaradhana became the king of Thanesar after both his father and elder brother died.
- Harshavardhana never got success in the east.
- Aihole was an important centre of trade.
- The capital cities of the Pallavas and Chalukyas were not very prosperous.
- The prathama-kulika meant the chief craftsman.
Answer:
- False
- False
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False.
IV.MATCHING SKILL Class 6 SST Question Bank
Match the items in column A correctly with those given in column B.
Column A Column B
(i) Kalidasa (a) The court poet of Pulakeshin II
(ii) Aryabhatta (b) The court poet of Samudragupta
(iii) Ravikirti (c) A renowned poet during this period
(iv) Harishena (d) The court poet of Harshavardhana
(v) Banabhatta (e) An astronomer
Ans. (i)—(c), (ii)—(e), (iii)—(a), (iv)—(b), (v)—(d).
Class 6 SST Question Bank BUILDINGS, PAINTINGS AND BOOKS ( 2 Marks )
2 very short answer type questions each of 1 mark will be covered from this chapter in annual Exam
1. Match the following: Class 6 SST Question Bank
| Stupa | Place where the image of the deity is installed. |
| Shikhara | Mound. |
| Mandapa | Circular path around the stupa. |
| Garbhagrika | Place in temples where people could assemble. |
| Pradakshina Patha | Tower. |
Answer:
| Stupa | Mound. |
| Shikhara | Tower. |
| Mandapa | Place in temples where people could assemble. |
| Garbhagriha | Place where the image of the deity is installed. |
| Pradakshina patha | Circular path around the stupa. |
4. Fill in the blanks: Class 6 SST Question Bank
- ………. was a great astronomer.
- Stories about gods and goddesses are found in the ……….
- ……… is recognized as the author of the Sanskrit Ramayana.
- ……….. and ……….. are two Tamil epics.
Answer:
- Aryabhatta
- Puranas
- Valmiki
- Silappadikaram, Manimekalai.
I.MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Class 6 SST Question Bank
Choose the correct option to complete the statements given below:
(i) The iron Pillar is situated at………………
(a) Junagarh
(b) Mehrauli
(c) Aihole
(d) Ahmedabad.
(ii) The height of the Iron Pillar is …………….
(a) 7.2 m
(b) 8.2 m
(c) 9.2 m
(d) 10.2 m.
(iii) The small box placed at the centre or heart of the stupa is known as a………………………
(a) Relic casket
(b) Sacred box
(c) Trunk
(d) None of the above.
(iv) The Puranas contained stories about …………………
(a) Kings and queens
(b) Gautam Buddha
(c) Mahatma Gandhi
(d) Gods and goddesses.
(v) Sanskrit Ramayana is written by ………………
(a) Valmiki
(b) Vyasa
(c) Tulsidas
(d) Vishnu Sharma.
Answer:
(i) – (b), (ii) – (a), (iii) – (a), (iv) – (d), (v) – (a).
II.FILL IN THE BLANKS Class 6 SST Question Bank
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence.
- The ………. at Aihole was built about 1400 years ago
- The small box placed at the centre of the stupa contains bodily remains of the and his followers.
- The……. were recited in temples by priests and people came to listen to them.
- Both the……….. and the…………. are supposed to have been composed by Vyasa.
- developed a scientific explanation for eclipses.
Answer:
- Durga temple
- Buddha
- Vedas
- Puranas, Mahabharata
- Aryabhatta
III.TRUE/FALSE Class 6 SST Question Bank
State whether these sentences are true (T) or false (F).
- Most temples of this period had a hall like structure known as the mandapa.
- Mahabalipuram and Aihole are known for the finest stone temples.
- Merchant and farmers usually decided to build stupas and temples during this period.
- The Tamil epic the Silappadikaram was composed by a poet named Ilango.
- Meghaduta is a famous poem composed by Tulsidas.
- Women and Shudras could hear the stories of the Puranas.
- It was Ravana who abducted Rama’s wife Sita.
- The Jatakas and the Panchatantra are collections of stories told by birds and animals.
- Aryabhatta was a famous story-letter.
- The Bhagavad Gita is a part of the Ramayana.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False.
IV.MATCHING SKILL Class 6 SST Question Bank
Match the items in column A correctly with those given in column B.

Ans. (i)—(b), (ii)—(d), (iii)—(a), (iv)—(e), (v)—(c).
Class 6 SST Question Bank– WHAT BOOKS AND BURIALS TELL US? (4 Marks)
CCT type question
Class 6 SST Question Bank– GLOBE: LATITUDES AND LONGITUDES (2 Marks)
Map Work (2 Marks)
2 questions related with maps will be asked from this chapter. Class 6 SST Question Bank
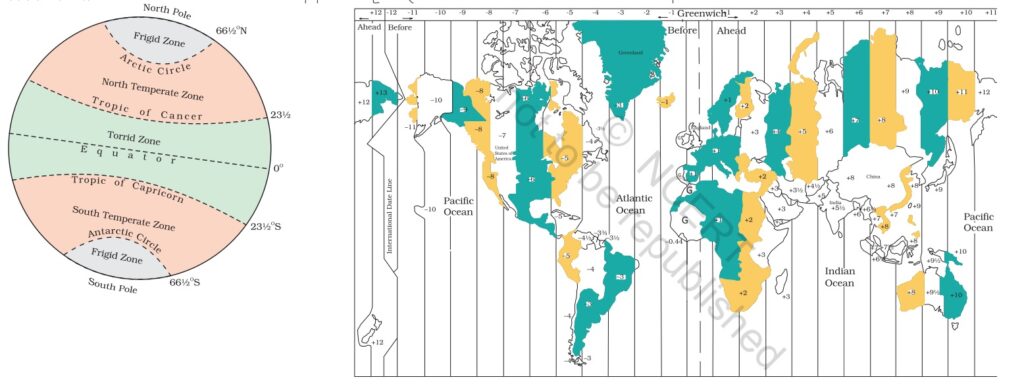
Class 6 SST Question Bank MAJOR DOMAINS OF THE EARTH
4 marks CCT question and 1 very short answer type question of 1 mark Class 6 SST Question Bank
Tick the correct answer. Class 6 SST Question Bank
(a) The mountain range that separates Europe from Asia is
(i) the Andes (ii) the Himalayas (iii) the Urals.
(b) The continent of North America is linked to South America by
(i) an Isthmus (ii) a Strait (iii) a Canal.
(c) The major constituent of the atmosphere by percent is
(i) Nitrogen (ii) Oxygen (iii) Carbon dioxide.
(d) The domain of the earth consisting of solid rocks is
(i) the Atmosphere (ii) the Hydrosphere (iii) the Lithosphere.
(e) Which the largest continent?
(i) Africa (ii) Asia (iii) Australia
Answers:
(a)—(iii)
(b)—(i)
(c)—(i)
(d)—(iii)
(e)—(ii).
3. Fill in the blanks. Class 6 SST Question Bank
The deepest point on the earth is ……….. in the Pacific Ocean.
The……… Ocean is named after a country.
The……… is a narrow contact zone of land, water and air that supports life.
The continents of Europe and Asia together are known as…………….
The highest mountain peak on earth is…………….
Answers:
Mariana Trench
Indian
Biosphere
Eurasia
Everest
Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct option to complete the sentences given below:
(i) Life exists in this zone:
(a) Lithosphere (b) Biosphere
(c) Hydrosphere (d) Atmosphere.
(ii) It is the only continent through which the tropic of Cancer, the Equator, and the Tropic of Capricorn pass:
(a) Asia (b) Europe
(c) Africa (d) North America.
(iii) It is the world’s longest mountain range
(a) The Mt. Everest (b) The Ural Mountains
(c) The Karakoram range (d) The Andes.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Major Domains of the Earth MCQs Q1
(iv)Which ocean is ‘S’ shaped?
(a) The Pacific Ocean (b) The Atlantic Ocean
(c) The Indian Ocean (d) The Arctic Ocean.
(v) Which one is not the layer of the Atmosphere?
(a) The Biosphere (b) The Troposphere •
(c) The Stratosphere (d) The Mesosphere.
(vi) It is called an island continent
(a) South America (b) Antarctica
(c) Africa (d) Australia.
Answers:
(i)— (b)
(ii)—(c)
(iii)—(d)
(iv)—(b)
(v)—(a)
(vi)—(d).
II. Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence:
The South Pole lies almost at the centre of………………..
Africa is the second largest continent after ……………..
The world’s longest river the Nile flows through ………………
The hydrosphere comprises water in the form of ………………., water and ………….
The Arctic Ocean is connected with the Pacific Ocean by a narrow stretch of shallow water known as ……………
The Pacific Ocean is …………. in shape.
The Coastline of the Atlantic Ocean is high……………….
Europe lies to the …………. of Asia.
Answers:
Antarctica
Asia
Africa
ice, water vapour
Berring Strait
circular
indented west.
Class 6 SST Question Bank – MAJOR LANDFORMS OF THE EARTH
From this chapter 2 question each of 1 mark will be asked from this chapter.
2. Tick the correct answer.
(a) The mountains differ from the hills in terms of
(i) elevation
(ii) slope
(iii)aspect.
(b) Glaciers are found in
(i) the mountains
(ii) the plains
(iii)the plateaus.
(c) The Deccan plateau is located in Class 6 SST Question Bank
(i) Kenya
(ii) Australia
(iii)India.
(d) The river Yangtze flows in
(i) South America
(ii) Australia
(iii)China.
(e) An important mountain range of Europe is ‘
(i) the Andes
(ii) the Alps
(iii) the Rockies.
Answer:
(a)-(i), (b)-(i), (c)-(iii), (d)-(iii), (e)-(ii).
3. Fill in the blanks.
A………… is an unbroken flat or a low-level land.
The Himalayas and the Alps are examples of…………………… types of mountains.
……… areas are rich in mineral deposits.
The………… is a line of mountains.
The ……….. areas are most producting for farming.
Answer:
plain
young fold
Plateau
range plain.
Choose the correct option to complete the sentences given below:
(i) It is the mountain range of South America.
(a) The Himalayas (b) The Alps
(c)The Andes (d) The Rockies.
(ii) Mt. Kilimanjaro is in
(a) Asia (b) Africa
(c) South America (d) North America.
(iii) Which one sport is not popular in the mountains?
(a) Paragliding (b) Skiing
(c) Hang gliding (d) Football.
(iv) The Hundru falls is in
(a) Chhotanagpur (b) Calcutta
(c) Ranchi (d) Chhattisgarh.
(v) The world’s highest plateau is the
(a) Deccan plateau (b) Tibet plateau
(c) Chhotanagpur plateau (d) East African plateau.
Answer: (i)—(c), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(a), (v)-(b).
II. Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence:
Many of the mining areas in the world are located in………………………….. areas.
The climate of mountains is …………………..
Mountains vary in their ……………….. and shape.
The Ural mountains in …………….. have rounded features and low elevation.
Volcanic mountains are formed due to …………………… activities.
The …………. and terraces are ideal for crop cultivation.
………… in the Pacific Ocean is an undersea mountain.
Fill in The Blanks
Answer:
plateau
harsh
heights
Russia
volcanic
river basins
Mauna Kea (Hawaii)
Class 6 SST Question Bank OUR COUNTRY- INDIA
2. Tick the correct answer.
(a) The southernmost Himalayas are known as …………….
(i) Shiwaliks
(ii) Himadri
(iii) Himachal.
(b) Sahyadris is also known as …………
(i) Aravali
(ii) the Western Ghats
(iii) Himadri.
(c) The Palk Strait lies between the countries ……………
(i) Sri Lanka and Maldives
(ii) India and Sri Lanka
(iii) India and Maldives.
(d) The Indian islands in the Arabian sea are known as ……………….
(i) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
(ii) Lakshadweep Islands
(iii) the Maldives
(e) The oldest mountain range in India is the ……………
(i) Aravali hills
(ii) the Western Ghats
(iii) Himalayas
Answer:
(a)—(i), (b)—(ii), (c)—(ii), (d)—(ii), (e)—(i)
3. Fill in the blanks.
India has an area of about…………..
The Greater Himalayas are also known as……………
The largest state in India in terms of area is……………..
The river Narmada falls into the……………
The latitude that runs almost halfway through India is ……………….
Answer:
3.28 million sq. km
Himadri
Rajasthan
Arabian
The Tropic of Cancer.
. Answer the following questions briefly.
(a) Name the major physical divisions of India.
(b) India shares its land boundaries with seven countries – Name them.
(c) Which two major rivers fall into the Arabian Sea?
(d) Name the delta formed by the Ganga and the Brahmaputra
(e) How many States and Union Territories are there in India? Which states have a common capital?
(f) Why do a large number of people live in the Northern Plains?
(g) Why is Lakshadweep known as a coral island?
Answer:
(a) Major physical divisions of India:
The Himalayas
The Northern Great Plains
The Peninsular Plateau
The Coastal Plains
The Islands
(b) Countries sharing land boundaries with India:
Pakistan
Afghanistan
China
Nepal
Bhutan
Myanmar
Bangladesh
(c) (i) Narmada
(ii) Tapi (Tapti)
(d) Delta formed by Ganga and Brahmaputra: Sunderban.
(e) States: 28, Union Territories: 07.
States of Punjab, Haryana and Union Territory of Chandigarh have a common capital at Chandigarh.
(f) Large number of people live in the Northern plains because of the following reasons:
Fertile land provides facilities for agriculture. It sustains more people.
Means of transport and communication are developed here. They provide mobility to people.
Opportunities for employment exist in the plains.
Water is easily available.
Industries provide employment (Agro-based industries)
(g) Lakshadweep is a coral island because of the following reasons:
Climate and seawater is suitable for the growth of polyps.
Their skeletons pile up and form islands.
Class 6 SST Question Bank -INDIA: CLIMATE, VEGETATION AND WILDLIFE
Answer the following questions briefly.
(a)Which winds bring rainfall in India? Why is it so important?
(b)Name the different seasons in India.
(c)What is natural vegetation?
(d)Name the different types of vegetation found in
(e)What is the difference between evergreen forest and deciduous forest?
(f)Why is tropical rainforest also called evergreen forest?
Answers:
(a) Monsoon winds bring rainfall in India. Agriculture in India depends on rains. Good monsoons mean sufficient rain and a good crop. Hence, monsoon winds Eire very importantly. Our prosperity depends on these winds.
(b) The different seasons in India are:
Cold Weather Season (Winter)
Hot Weather Season (Summer)
Southwest Monsoon Season (Rainy)
Season of retreating Monsoon (Autumn).
(c) Natural Vegetation
Grasses, shrubs, and trees which grow of their own without any interference or help from mankind constitute natural vegetation.
(d) Different types of vegetation found in India
Tropical Rain Forests
Tropical Deciduous Forests
Thorny Forests
Mountain Vegetation
Mangrove Forests
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 8 India Climate Vegetation and Wildlife Q1
(f) Tropical rainforest is also called evergreen forest because they (the trees) do not shed their leaves in a particular season.
2. Tick the correct answer.
(a) The world’s highest rainfall occurs in …………
(i) Mumbai (ii) Asansol (iii) Mawsyuram.
(b) Mangrove forests can thrive in………
(i) saline water (ii) freshwater (iii)polluted water.
(c) Mahogany and rosewood trees are found in………..
(i) mangrove forests
(ii) tropical deciduous forests
(iii) tropical evergreen forests
(d) Wild goats and snow leopards are found in…………
(i) Himalayan region (ii)Peninsular region (iii) Gir forests.
(e) During the South-west monsoon period, the moisture-laden winds blow from
(i) land to sea (ii) sea to land (iii) plateau to plains.
Answers:
(a)—(iii), (b)—(i), (c)—(iii), (d)—(i), (e)—(ii).
3. Fill in the blanks.
Hot and dry winds are known as………… blow during the day in summers.
The states of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu receive a great amount of rainfall during the season of…………..
……. forest in Gujarat is the home of……………
…………… is a well-known species of mangrove forests.
…………. are also called monsoon forests.
Answer:
loo
retreating monsoon
Gir, Asiatic lions
Sundari
Tropical deciduous forests.
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct option to complete the statements given below:
(i) Sundarbans is in ………..
(a) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
(b) West Bengal
(c) Orissa
(d) Madhya Pradesh.
(ii) Which one forms the group of migratory birds?
(a) Siberian Crane, Flamingo and Crow
(b) Sparrow, Crow, and Stork
(c) Stork, Siberian Crane, and Flamingo
(d)Duck, Bulbul and geese.
(iii) These places experience moderate climate ………………
(a) Mumbai and Kolkata
(b) Patna and Lucknow
(c) Bikaner and Jaisalmer
(d) Ranchi and Asansol.
(iv) Elephants and one-homed rhinoceroses are found in the forests of……………………
(a) Assam
(b) Gujarat
(c) Kerala
(d)Karnataka
(v) Wildlife week is observed every year in the first week of _________
(a) November
(b) August
(c) September
(d) October.
Answers: (i)—(b), (ii)—(c), (iii)—(a), (iv)—(a), (v)—(d).
Class 6 SST Question Bank – Social and Political life–What is Government ?
Choose the correct option to complete the statements given below: Class 6 SST Question Bank
(i) The government also works at the local level. Here local level means Class 6 SST Question Bank
(a) Village
(b) Town
(c) Locality
(d) All the above.
(ii) The court can intervene if…………….. Class 6 SST Question Bank
(a) Any law passed by the government is not followed.
(b) Anyone does not study well.
(c) A child tells a lie
(d) Both (a) and (b).
(iii) American women got the right to vote in the year………………….. Class 6 SST Question Bank
(a) 1928
(b) 1925
(c) 1920
(d) 1919
(iv) The term suffrage means ………………. Class 6 SST Question Bank
(a) Right to vote
(b) Right to go anywhere in the country
(c) Right to livelihood
(d) None of the above.
(v) The two types of government mentioned the chapter are: Class 6 SST Question Bank
(a) Democracy
(b) Monarchy
(c) Dictatorship
(d) (a) and (b).
Answer:
(i) – (d), (ii) – (a), (iii) – (c), (iv) – (a), (v) – (d).
II. FILL IN THE BLANKS
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence. Class 6 SST Question Bank
- The government works at different levels at the local level, at the level of the state and at the ………… level.
- In a………. the government has to explain its actions and defend its decisions
to the people. - Women in the UK got the right to vote in the year…………………..
- In India, before Independence, only a small minority was allowed to ………………………
- …….. are also part of the government.
Answer:
- national
- democracy
- 1928
- vote
- Courts.
Class 6 SST Question Bank – Urban Administration
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct option to complete the statement given below. Class 6 SST Question Bank
(iv) Which one is not the job of the Municipal Corporation? Class 6 SST Question Bank
(a) It keeps the streets and markets clean.
(b) It makes gardens and maintains them.
(c) It builds hotels for the tourists
(d) It runs schools, hospitals, and dispensaries.
(v) The Municipal Council is found in
(a) Big cities
(b) Small towns
(c) villages
(d) Metropolitan cities.
Answer:
(i) – (d), (ii) – (a), (iii) – (c), (iv) – (c), (v) – (b).
II.FILL IN THE BLANKS
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence: Class 6 SST Question Bank
- Property taxes form only ……………. percent of the money that a Municipal Corporation earns.
- Collecting garbage is quite a………… job.
- The kabaddi wallah plays a major role in ………………. household plastic and paper.
- The Ward Councillor is elected by the people of his ………………
- Gangabai rushed to the house of………………
Answer:
- 25-30
- dangerous
- recycling
- Ward/area
- Ward Councillor.
III.TRUE/FALSE
State whether these sentences are true (T) or false (F). Class 6 SST Question Bank
- Gangabai was a timid lady.
- Yasmin Khala was a retired judge.
- Pune, being a big city, has a Municipal Corporation.
- Larger houses have to pay fewer taxes.
- The Commissioner and the administrative staff implement the decisions taken by the Councillor’s Committees and the councillors. Class 6 SST Question Bank
Answer:
- F
- F
- T
- F
- T
V .SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS Class 6 SST Question Bank
1. How are complicated decisions taken? Explain with examples. [V. Imp.] Class 6 SST Question Bank
Ans: (Complicated decisions usually affect the entire city and therefore these decisions are taken by groups of Councillors who form committees to decide and debate issues. For example, if bus stands need to be improved or a crowded market place needs to have its garbage cleared more regularly, etc.
2. Write a short note on the topic ‘Sub-contracting’. [Imp.] Class 6 SST Question Bank
Ans: In recent times, in order to save money the Commissioners of several municipalities across the country had hired private contractors to collect and process garbage. This is known as Sub-Contracting. This means that the work that was earlier being done by government workers is now being done by a private company or agency. These contract workers get low salary and their jobs are temporary.
1. Explain the Junctions of the Ward Councillor and the Administrative staff. Class 6 SST Question Bank
Ans: The Ward Councillors are elected members. They are responsible for the welfare of the people of their wards. They listen their problems and get them solved. Sometimes, they have to take complicated decisions that affect the entire city. At such moments, groups of councillors who form committees gather together to decide and debate issues. While the Councillor’s Committees and the councillors decide on issues, the Commissioner and the administrative staff implement these decisions.
All of the Ward Councillors meet and they make a budget and the money is spent according to this. The Ward Councillors try and ensure that the particular demands of their wards are placed before the entire council. These decisions are then implemented by the administrative staff.
Class 6 SST Question Bank–Rural Livelihoods
Choose the correct option to complete the statements given below: Class 6 SST Question Bank
(i) Ramalingam has …………
(a) Thirty acres of land
(b) Twenty acres of land
(c) Ten acres of land
(c) Five acres of land
(ii) Thulasi earns ………..
(a) Rs. 40 per day
(b) Rs. 60 per day
(c) Rs. 70 per day
(d) Rs. 100 per day
(iii) Thulasi sold her cow to ………
(a) Purchase jewellery
(b) Pay the instalment of the loan that she took from bank
(c) Pay the fees of her daughter
(d) Pay back the money she borrowed from Ramalingam.
(iv) The percentage of large farmers in India is ………….. Class 6 SST Question Bank
(a) 80
(b) 20
(c) 10
(d) 5
(v) Which one is not a farming activity? Class 6 SST Question Bank
(a) Ploughing (b) Harvesting
(c) Basket making (d) Weeding.
Answer:
(i) – (b), (ii) – (a), (iii) – (c), (iv) – (b), (v) – (c).
II.FILL IN THE BLANKS Class 6 SST Question Bank
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence: Class 6 SST Question Bank
- The people of Chizami village do ………………………………………….. farming.
- Nearly ……. of all rural families are agricultural labourers in India.
- Sekar has a hybrid cow, whose milk he sells in the local ………………
- In some villages in central India, both farming and ……………….. from forest are important sources of livelihood.
- The people of Pudupet village earn their living by………………
Answer:
- terrace
- two fifth
- milk cooperative
- collection
- fishing
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS Class 6 SST Question Bank
1. Describe different types of work that Sekar do for a living. [Imp.] Class 6 SST Question Bank
Ans: Sekar is a small farmer having only two acres of land. He grows paddy in his field with the help of his family members. He also works in Ramalingam’s rice milk. He helps him collect paddy from other farmers is the neighbouring villages. He also has a hybrid cow, whose milk he sells in the local milk cooperative.
2. List the three situations in which crops can be ruined. [V. Imp.] Class 6 SST Question Bank
Ans: The three situations in which crops can be ruined are :
- If the seeds are not of good quality.
- If pests attack the crop.
- If the monsoon does not bring enough rain.
3. Write a brief note on the lifestyle of the people of Chizami.
Ans: Chizami is a village in Phek district in Nagaland. The people of this village do terrace farming. They have their own individual fields. But, they also work collectively in each other’s fields. They form groups of six or eight and take an entire mountain side to clean the needs on it. Each group eats together once their work for the day is over.
1. Write a short note on the lives of fishing families. [V. Imp.] Class 6 SST Question Bank
Ans: Fishing families usually live close to the sea. Their lives revolve around the sea and fish. One can find rows of catamarans and nets lying around their houses. Their day usually starts from 7 O’clock in the morning. This is the time when there is a lot of activity on the beach. After catching fish the fishermen return with their catamarans. Women then gather to buy and sell fish. They do not go to the sea for at least four months during the monsoon because this is when the fish breed.
During these months they survive by borrowing from the trader. And thus, they are forced to sell the fish to that trader later on.The lives of fisherfolk are full of risks. Whenever there is a storm, they have to suffer a lot. In 2004, the tsunami hit them badly. They were the worst sufferers.
2. What different activities are done by the people of Kalpattu village? Class 6 SST Question Bank
Ans: Kalpattu is coastal village in Tamil Nadu. As the village is surrounded by low hills, paddy is the main crop here. Most of the families earn a living through agriculture. Besides agriculture, people do many non-farm activities such as making baskets, utensils, pots, bricks, bullock carts, etc. The village has no dearth of service providers like blacksmiths, nurses, teachers, washermen, weavers, barbers, cycle repair mechanics and so on.
One can find here shopkeepers and traders too. There is a bazaar where a variety of small shops such as tea shops, grocery shops, a tailor, seed shop etc. can be found. There are some coconut groves around the village. A group of people earn their living by working in mango orchards. In the village, there are small farmers as well as big farmers. There are landless labourers too who work in other’s field.
3. Under which circumstances poor farmers find themselves unable to pay back their loans? What happens after that? Class 6 SST Question Bank
Ans: Poor farmers are bound to take loans for agriculture purpose. Sometimes they successfully pay back the loans but there are also moments when they fail to do that in time because of crop failure. This is a very tough time for them. For the family to survive, they have to borrow more money. Soon the loan becomes so large that no matter what they earn, they are unable to repay. This is when we can say they are caught in debt. Whenever this situation occurs, farmers become helpless. Their helplessness to repay the loan sometimes compel them to commit suicide.
Urban Livelihoods
1. How do hawkers manage their work? [V. Imp.] Class 6 SST Question Bank
Ans. Hawkers work on their own. They organise their own work. They know how much to purchase, as well as where and how to set up their shops. Their shops are usually temporary structures. Sometimes just some boards or papers spread over discarded boxes or may be canvas sheet hung up on a few poles. They may also use their own carts or simply a plastic sheet spread on the pavement. They can be asked to dismantle their shops at any time by the police.
2. Mention some drawbacks of casual jobs. [V. Imp.] Class 6 SST Question Bank
Ans. • In casual jobs, workers are not expected to complain about their pay or working
conditions. If they dare to do this, they are instantly asked to leave.
- Casual jobs do not provide security protection if there is ill-treatment.
- Casual workers are expected to do work for long hours.
Even if they don’t complain, they can be asked to leave when workload is less.
3. What works does Sudha do?
Ans. Sudha works as a Marketing Manager in a company which manufactures biscuits. The factoiy where the biscuits are made is outside the city. Sudha supervises the work of 50 salespersons who travel to different parts of the city. They get orders from shopkeepers and collect payments from them. She has divided the city into six regions and once a week she meets the salespersons of each region. She checks their progress report and discusses problems they face. She has to plan the sales in the entire city and often has to work late and travel to different places.
1. What are various ways of earning livelihood in the urban areas? Discuss. [V. Imp.]Class 6 SST Question Bank
Ans. People in urban areas are engaged in a variety of activities in order to earn their living. Some are doing the work of a cobbler while some are barbers busy with their work. A number of people earn their livelihood by pulling rickshaw. Vendors are also seen here and there selling household articles. In urban areas showrooms of different items can be seen. These showrooms are run by businesspersons. These people employ a number of workers as supervisors and helpers for their showrooms. Several urban people are engaged in Factories where they work for long hours.
They don’t have job security still they continue their work because they don’t have other option. But there are also people who do office work with full job security. They get regular salary and enjoy other benefits of job like savings for old age, holidays, medical facilities etc.
Working in Call Centres is a new form of employment in big cities. It has attracted a large number of young men and women. Thus, we see that with a growing population, job opportunities have also increased and people are availing these opportunities according to their talent and aptitude.
2. Write in brief on ‘Call Centres’.
Ans. Call Centres in big cities are providing new job opportunities to young and enthusiastic men and women. A Call Centre is a centralised office that deals with problems and questions that consumers/customers have regarding goods purchased and services like banking, ticket booking, etc. Call Centres are generally set up as large rooms with work stations that include a computer, a telephone set and supervisor’s stations.
Class 3 Session Ending Exam
- Class 3 Hindi Session Ending Exam
- Class 3 English Session Ending Exam
- Class 3 Maths Session Ending Exam
- Class 3 EVS Session Ending Exam
Class 4 Session Ending Exam
- Class 4 Hindi Session Ending Exam
- Class 4 English Session Ending Exam
- Class 4 Maths Session Ending Exam
- Class 4 EVS Session Ending Exam
Class 5 Session Ending Exam
- Class 5 Hindi Session Ending Exam
- Class 5 English Session Ending Exam
- Class 5 Maths Session Ending Exam
- Class 5 EVS Session Ending Exam
HINDI-RIMJHIM LESSON PLAN LINKS
- CLASS 1 HINDI RIMJHIM LESSON PLAN
- CLASS 2 HINDI RIMJHIM LESSON PLAN
- CLASS 3 HINDI RIMJHIM LESSON PLAN
- CLASS 4 HINDI RIMJHIM LESSON PLAN
- CLASS 5 HINDI RIMJHIM LESSON PLAN
ENGLISH-MARIGOLD LESSON PLAN LINKS
- Class 1 ENGLISH MARIGOLD LESSON PLAN
- Class 2 ENGLISH MARIGOLD LESSON PLAN
- Class 3 ENGLISH MARIGOLD LESSON PLAN
- Class 4 ENGLISH MARIGOLD LESSON PLAN
- Class 5 ENGLISH MARIGOLD LESSON PLAN
EVS-LOOKING AROUND LESSON PLAN LINKS
- CLASS 1 EVS LOOKING AROUND LESSON PLAN
- CLASS 2 EVS LOOKING AROUND LESSON PLAN
- CLASS 3 EVS LOOKING AROUND LESSON PLAN
- CLASS 4 EVS LOOKING AROUND LESSON PLAN
- CLASS 5 EVS LOOKING AROUND LESSON PLAN
